Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
2D Scatter¶
Scatter data in two dimensions.
The x-axis and y-axis define the coordinates of the scattered points.
@NX_class = "NXroot"
@default = "scan1"
scan1:
@NX_class = "NXentry"
@default = "data"
data:
@NX_class = "NXdata"
@x_indices = [0]
@y_indices = [0]
@signal = "z"
x: NX_FLOAT64[500]
y: NX_FLOAT64[500]
z: NX_FLOAT64[500]
Explanation:
@axesis omitted since default axes are not applicable.zis the default signal to be plotted versusxandy.Each data point in
zhas a coordinate inxandy.
Note that the NXdata structure does not describe how the data needs to
be plotted. In this example we create a 2D scatter plot in the XY-plane.
But the data could also be plotted as a function of x or y in a
Curve plot. When defining
@axes="x" the curve plot would be the most likely intention of the data
publisher but it is up to the reader to decide how to plot the data.
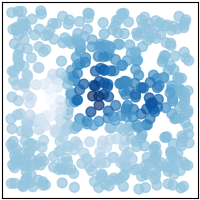
# Data
import numpy as np
rstate = np.random.RandomState(42)
x = rstate.uniform(-3, 3, 500)
y = rstate.uniform(-3, 3, 500)
z = (1 - x / 2 + x**5 + y**3) * np.exp(-(x**2) - y**2)
# Plot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa E402
plt.style.use("_mpl-gallery-nogrid")
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(x, y, c=z, s=50, alpha=0.7)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.065 seconds)
